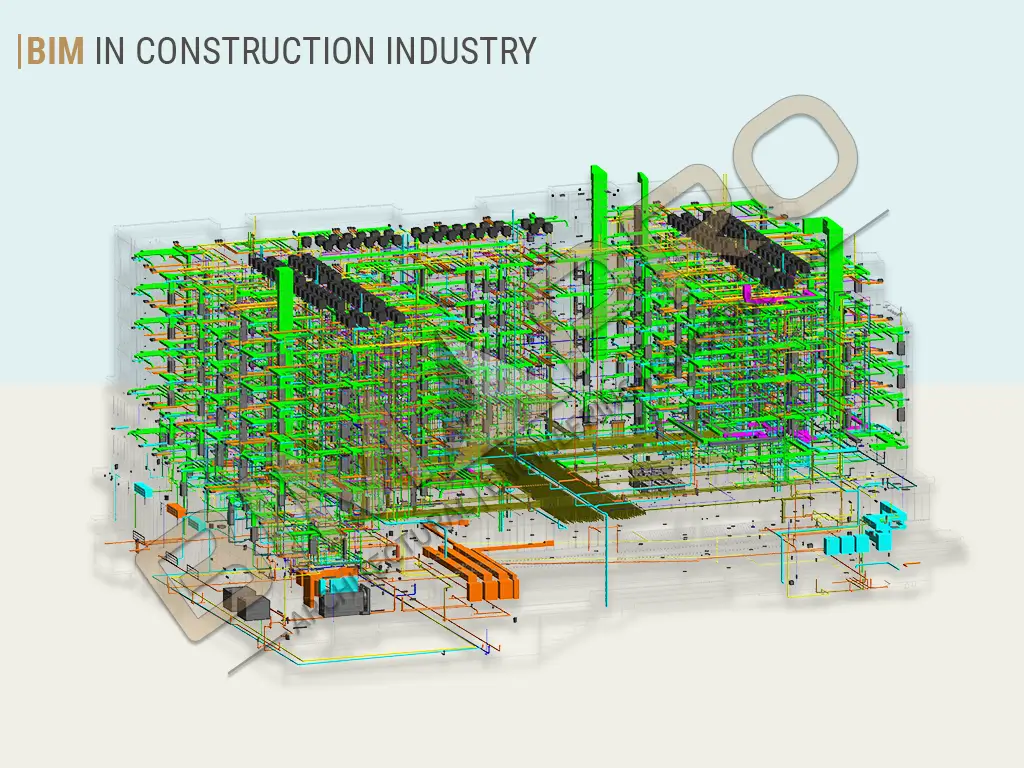
BIM in Construction Industry
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has had a profound impact on the construction industry, revolutionizing the entire process of project planning, design, and construction. BIM offers a digital 3D representation that captures both the physical and functional aspects of a building’s facility. This technology encompasses detailed geometric and semantic information from various architectural, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing), and structural disciplines, all seamlessly integrated to create a comprehensive 3D BIM model of the structure.
One of BIM’s key strengths lies in fostering collaborative efforts among all stakeholders involved in design and construction, including architects, engineers, general contractors, and trade contractors. This collaboration takes place within a shared digital BIM platform.
BIM’s transformative impact on the construction industry extends to numerous areas. It enhances team collaboration, optimizes design, detects clashes, estimates costs, manages scheduling, and streamlines facility management. The adoption of BIM within the construction sector continues to grow steadily. This is primarily due to construction companies recognizing the manifold advantages it offers, including improved project outcomes, risk mitigation, cost savings, shortened turnaround times, and heightened efficiency throughout the building’s lifecycle.
BIM Uses in the Construction Phase
BIM uses refer to the practical applications derived from the BIM process. The essential applications of BIM in the construction industry are introduced and further explained below:
- Existing Conditions Modeling or Field Capturing
A 3D model can be created to represent the current state of a site, a facility, or a specific space. Various techniques, such as modeling software, laser scanning, and surveying methods, can be employed to develop this model. The choice of method depends on project requirements and objectives. Laser scanning, for instance, generates an exceptionally precise 3D point cloud. This data can then be integrated into the BIM model and used either to model the area accurately or to validate existing models.
Explore: Point Cloud Scan to BIM Services
- Cost Estimation or Quantity Takeoff
A BIM 3D model is valuable for generating precise quantity takeoffs of building materials and components. The 3D model is connected to cost data, enabling the extraction of accurate cost estimates.
- 4D Modeling
4D modeling is a process utilized to plan and visualize the phased occupancy of construction projects. This technique proves particularly valuable for tasks like renovation, addition, retrofitting, or any project requiring coordinated sequencing of construction activities. The essence of a 4D model lies in integrating the traditional 3D building model with the dimension of time. This integration empowers stakeholders to not only visualize the project’s construction sequence but also to gain a comprehensive understanding of its execution and scheduling.
Explore: 4D Construction Simulation Services
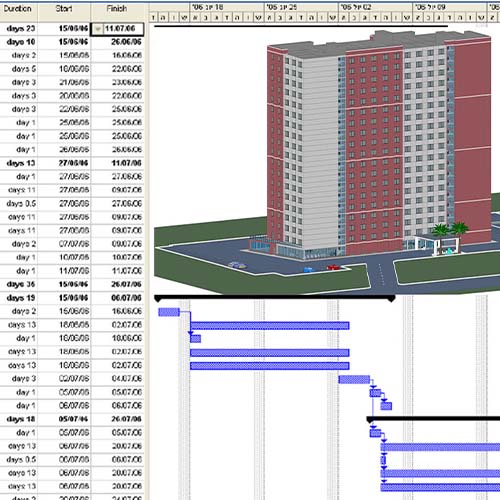
- Site Utilization Planning
By connecting the information from the 3D model with the 4D schedule, project stakeholders can efficiently communicate spatial and sequencing requirements at the construction site. This integration fosters a clearer comprehension of how diverse elements come together over time, aiding in the early detection of potential conflicts or constraints that might arise during the construction process.
- 3D Coordination and Clash Detection
Clash detection software is a valuable tool used in the construction industry to coordinate and identify clashes or conflicts between different building systems. It compares the 3D models of various systems, such as architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing, to detect any clashes before the actual construction or installation takes place.
Explore: BIM Coordination Services and Clash Detection Services
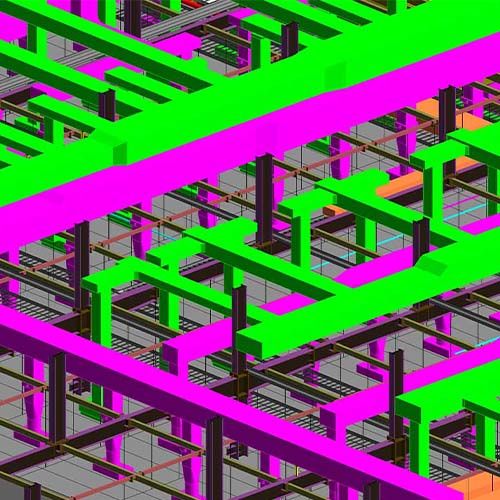
- Construction System Design or Virtual Mock-up
3D modeling software is widely used in the construction industry to create, design, and analyze building systems. It enables the detailed development of 3D representations for various components like formwork, glazing, tie-backs, and more.
A significant focus when using this software is on the connections between different building elements. These crucial junctions require collaboration and coordination across various trades. The software allows for in-depth analysis of these connection points.
- Digital Fabrication
Thanks to BIM technologies, digital fabrication minimizes uncertainties during manufacturing and provides clear instructions for component production, reducing waste. Manufacturers can accurately translate design plans into fabrication instructions, minimizing errors and enhancing efficiency. This technology is applied in areas such as sheet metal fabrication, structural steel fabrication, pipe cutting, and 3D printing for prototyping.
Explore: Shop Drawings Services
- 3D Control and planning or Digital Layout
Information models are used to position facility components and automate equipment control and movement.
- Field/Manage Tracking
During construction, commissioning, and handover, Field Management BIM software helps manage tasks, quality control, safety, and document reporting. It’s connected to BIM models and ensures smooth processes.
- Record Modeling or As-built Modeling
Record modeling accurately portrays the physical conditions, environment, and assets of a facility. It combines BIM models created during design, construction, 4D coordination, and subcontractor fabrication to deliver a comprehensive record model for owners and facility managers.
Why BIM is Important to Construction Managers?
While the design team is often associated closely with Building Information Modeling (BIM), Construction Managers (CM) also play a vital role in ensuring a successful construction project. Even though CMs typically don’t create the BIM model itself, they need a solid grasp of the procedures and technologies used throughout the project’s entire lifespan, not just the design phase.
It’s crucial to oversee the asset from its creation to its operation and eventual decommissioning. Construction managers must understand BIM data thoroughly, contribute to it, and verify its accuracy to make the most of its benefits. They need to use model information and innovative approaches to support new construction techniques, scheduling, costs, quality, coordination, fabrication, sequencing, facilities management, and more. To fulfill these broader responsibilities, construction managers need to embrace new tools, processes, and skills
Benefits of BIM for Contractors
BIM has become a valuable method in the construction industry, offering several benefits that general contractors and subcontractors implement for efficient project outcomes.
- Enhanced Planning and Design
BIM enables contractors to collaborate closely with architects and engineers during the project’s planning and design phase. This collaboration allows contractors to provide input on constructability and cost-effective solution
- Streamlined Coordination
BIM improves coordination among various trades by integrating architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing models in platforms like Navisworks. This integration detects clashes and resolves conflicts before construction starts.
- Accurate Cost Estimation
General contractors and subcontractors can extract accurate quantities of building materials directly from detailed BIM models. This eliminates manual calculations and errors, ensuring precise bidding and procurement.
- Advanced Construction Simulation and Scheduling
BIM allow platform to integrate construction simulation and scheduling data with the 3D BIM model. This help owners, contractors to optimize project timelines, plan resources, ensuring efficient project execution.
- On-site Construction Management
BIM allow real time onsite access in digital model which allow contractors to monitor the accurate installation, verify compliance with design intent, and track construction progress.
Conclusion
References
Read More Related Blogs
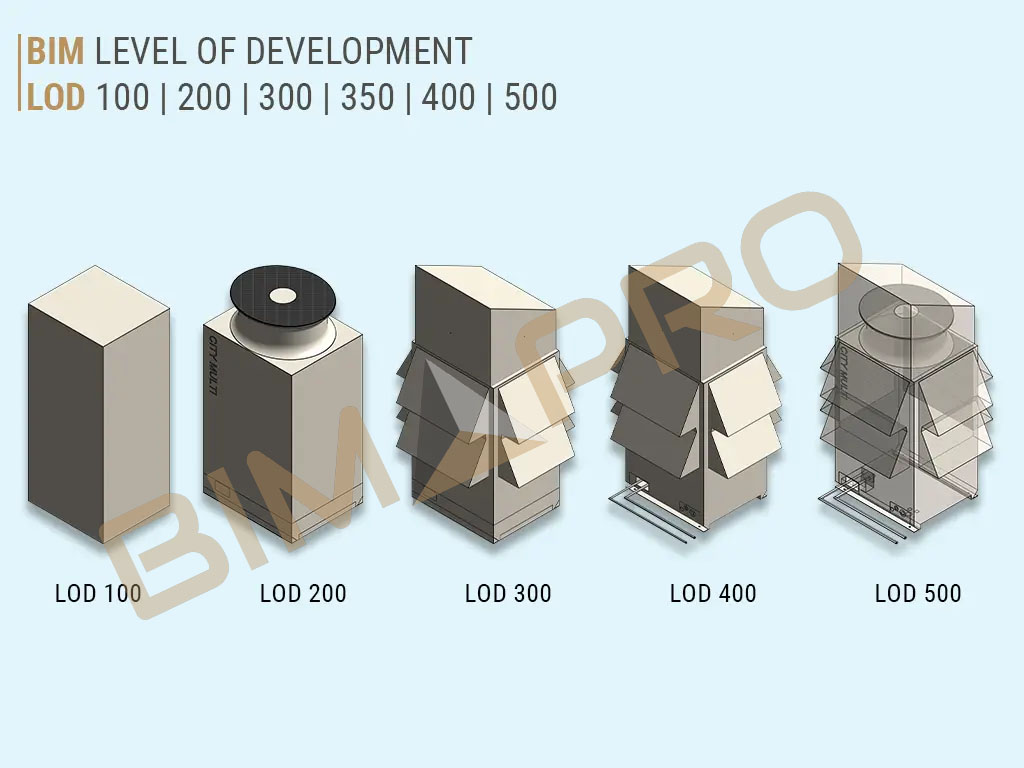
This BIM LOD (Level of Development) blog seeks to address the concept and understanding about LOD in AEC industry with clear guidance …
BIM implementation is increasingly gaining traction. The architecture, engineering, construction, and operations (AECO) industry across United States is rapidly transitioning to a digital …
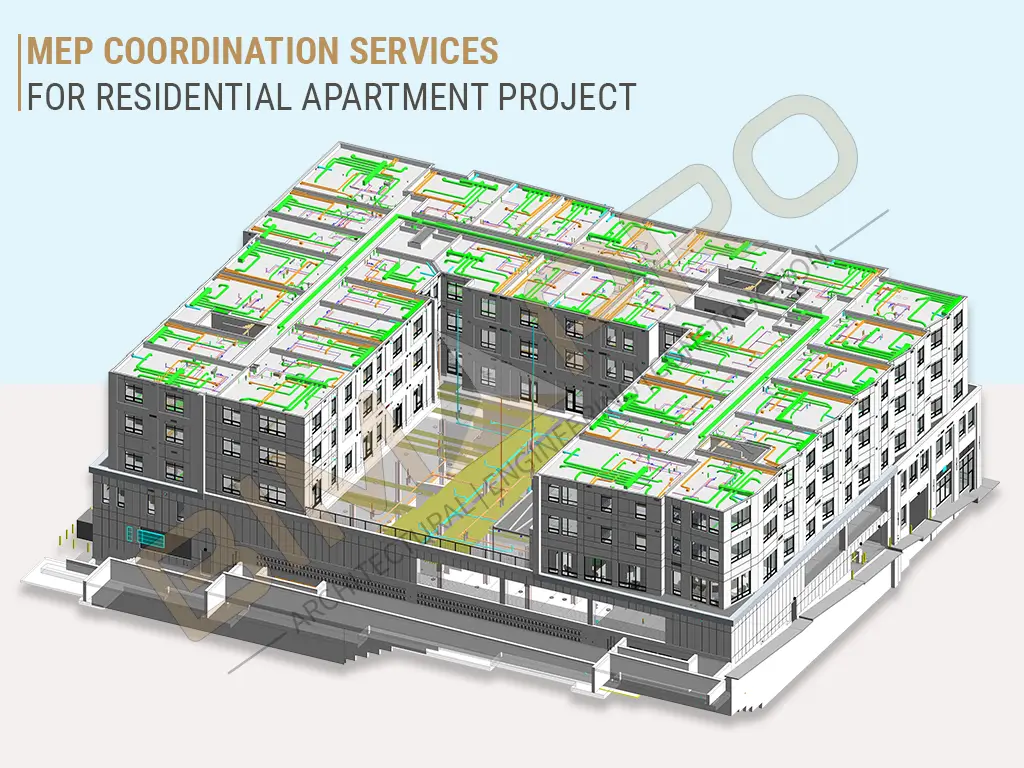
Setup of MEP coordination services framework presents a significant challenge for complex Apartment projects. Today, residential projects are so complex that specialized …